


Responsible researcher: Eduarda Miller de Figueiredo
Title of the article: INSTITUTIONAL SCHOLARSHIP PROGRAM FOR STARTING TEACHING (PIBID): PERFORMANCE OF SCHOLARSHIPS VERSUS NON-SCHOLARSHIPS
Authors of the article: Adriana Castro Araujo, Wagner Bandeira Andriola and Afrânio de Araújo Coelho
Location of intervention: Federal University of Ceará
Sample Size: 2.193
Big theme: Education
Type of Intervention: Evaluate the efficiency of PIBID
Variable of main interest: Academic Achievement Index (ARI)
Assessment method: Others – descriptive field research
Policy Problem
According to Andriola (2012), learning is a “qualitative and stable behavioral change, occurring in the mental processes of memorization, understanding, application, analysis, synthesis and judgment, among others”. This process is included in the student's training.
The Institutional Teaching Initiation Scholarship Program (PIBID) is a public teacher training policy, where its main objective is to attract better professionals to work in public schools, contributing to an improvement in public basic education in the country. Thus, the program was established through article 62, paragraph 5 of the National Education Guidelines and Bases Law (LDB), with the aim of encouraging teaching, encouraging a teaching career in public basic education. Although PIBID has demonstrated success in its objectives, the problems that exist in basic education in Brazil still hinder the recruitment of teachers with higher qualifications (ARANTES, 2013).
Implementation and Evaluation Context
The intention of evaluating the program is to obtain diagnoses that will enable the planning of actions for its improvement, in addition to assisting in decision-making by managers and public policy makers (ANDRIOLA, 1999). Since it is in the evaluation phase that it is possible to verify whether the primary objectives have been achieved, improve actions and decide whether the program will be continued or a new one created (FREY, 2000).
This type of evaluation is extremely important for higher education, as the program is included in a sphere of public policies for education. Therefore, it becomes necessary to observe its effects from the point of view of “inspection processes and educational quality” (SOUSA et al., 2016). Therefore, the PIBID evaluation will take place at the Federal University of Ceará (UFC), where the program includes the degrees typified in the CAPES notice [1] as priorities. The subjects are Biological Sciences, Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics and Philosophy. In addition to the subject of Literature-Portuguese, which would contribute to other areas by improving understanding, reading and writing.
Policy Details
PIBID served around 3 thousand fellows when it started in 2007. In 2011 this number reached almost 30 thousand and, currently, it has more than 90 thousand fellows. Specific evaluations of the program demonstrate effects in relation to students' motivation to become teachers and in relation to improving the training of professionals who are supervisors of students participating in PIBID (ANDRÉ, 2012). Furthermore, Silveira (2013) observed that university students understood that the practice of teaching goes beyond mastering the content given in the classroom.
The PIBID evaluation will take place at the Federal University of Ceará (UFC), where the program includes the degrees typified in the CAPES notice [1] as priorities. The subjects are Biological Sciences, Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics and Philosophy. In addition to the subject of Literature-Portuguese, which would contribute to other areas by improving understanding, reading and writing.
Assessment Method
The objective of the article is to evaluate and compare the academic performance of PIBID scholarship holders and non-scholarship holders, through the Academic Performance Index (IRA) that UFC calculates in each subject studied through evaluations of the scholarship holder's academic performance. In addition, the course's grade in the National Student Performance Exam (ENADE) and the course's operating shift are also taken into account.
To this end, descriptive field research was carried out with 2,193 undergraduate graduates from the Federal University of Ceará from 2009/2 to 2015/1. From this sample, the group of former PIBID fellows was compared, representing a total of 209 individuals (12.3% of the sample), with the 1,924 non-fellowship holders (87.7% of the sample).
Results
PIBID scholarship holders showed homogeneity in academic performance in contrast to non-scholarship holders, especially in courses with the highest ENADE concept. When the ENADE concept is not observed, the average values of the Academic Performance Index (ARI) of the program's scholarship holders present higher values. As per the graph below:
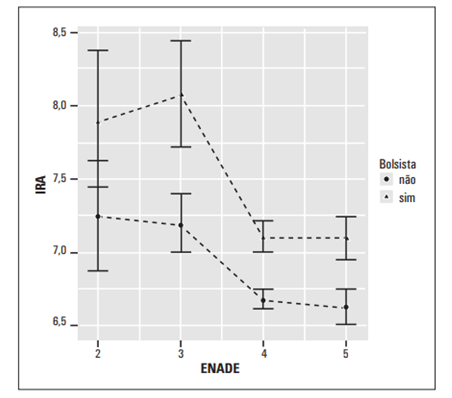
With this difference in IRA, the authors were able to observe that PIBID scholarship holders developed their cognitive abilities and assimilation of curricular content better, compared to non-scholarship holders.
In relation to course shifts, the study was able to observe that the IRA was always lower in day shift courses, compared to mixed or night shift courses. Furthermore, the results continue to confirm that regardless of the undergraduate course's operating shift, PIBID scholarship holders achieve academic performance that is qualitatively superior to non-scholarship holders.
The results found in this article corroborate studies such as that by Darroz and Wannmacher (2015), which also highlighted the benefits of PIBID in the training of university scholarship holders. Therefore, PIBID has been a program that provides opportunities and enriches learning.
Public Policy Lessons
The positive results demonstrated in the study show the importance of the Institutional Teaching Initiation Scholarship Program for the training of university students. These, in addition to obtaining better academic performance, with substantial differences in the quality of learning of their fellows, encouraged the practice of teaching.
As the authors mention in the article, Albert Einstein once said “ I don't teach my students. I create conditions for them to learn ”. This would be the essence of PIBID, which has been fulfilled. After all, the program has added value to the training of students, enriching them with experiences so that, in the future, they can become professionals in the art of teaching.
[1] CAPES – Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel.
[1] CAPES – Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel.